Geriatric Rehabilitation Treatment
What is geriatric rehabilitation?
Geriatric rehabilitation is the physiotherapy care for the elderly. We all have an elderly person at our home who is in the need to be taken care of. Our grandfathers, grandmothers even our parent’s are growing old and need attention love as well as care.
By the word “geriatric”, individuals are categorized into ages greater than 65 years in this category. But it is only after the age of 70 the individuals need geriatric rehabilitation.
Ageing affects individuals differently. It all depends on the physiological age which shows exactly how the body is reacting to degeneration caused by ageing.
As normal aging does not come with disabilities but many elderly suffer from a disability which is associated with a condition. As a person ages the degeneration takes place in the body. All the individuals notice a decline in lung function because physiologically the lung capacity decreases with age.
Similarly, the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system, nervous system and brain, immune system, get affected by ageing. Ageing overall may result in various conditions like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, nervous disorders, degenerative joint disorders, etc. These disorders turn into disabilities if not treated on time. The age group of the oldest, 85 years and older have a high percentage of disabilities and upto 40 percent of all elderly are over 65 years of age. Goals of Geriatric Rehabilitation The prime goal of geriatric rehabilitation in elderly is the development of a sense of independence and the physical ability to do tasks of daily living.
There are some aspects that are taken into consideration in the rehabilitation of geriatric patients:
- Reactivation – The sick elderly persons must adapt to the situation and improve as much as possible and must acquire the ability to take care of themselves by being independent, focusing on total recovery from a condition as old age and degeneration cannot be reversed. Improving overall health is very important.
- Social reintegration – Elderly patients must return to where family and friends are located instead of living alone, avoiding isolation can solve many problems related to mental health issues. Reinstatement into society- interacting and participating in the society is beneficial. Participating in moderate professional activities and learning new skills gives a sense of purpose and keeps the brain healthy.
- Low physical demand activities like walking, handcraft, or hobbies like gardening are beneficial in maintaining the physical activity corresponding to their residual capacity. Effects of Ageing The skeletal muscle strength begins to decline rapidly at approximately age 45 years, as individuals start to lose the muscle mass. It is associated with a 30% to 40% decrease in strength by the age of 80 years.
- The loss of muscle mass not only causes a reduction in strength as well in the range of motion of joints. It may also be responsible for upto 30% of the decline in maximal rate of O2 consumption of the muscles. The loss of skeletal muscle mass below a critical level is known as sarcopenia. It leads to functional impairment and frailty.
- Many studies suggest that muscle loss is common and highly correlated with the decreased function in older adults. Approximately 8% of men and 10% of women had values of muscle mass below two standard deviations of young adult values (class II sarcopenia). It has been established that sarcopenia, characterized by diminished muscle mass, strength, and power, is a key common denominator in the development of frailty.
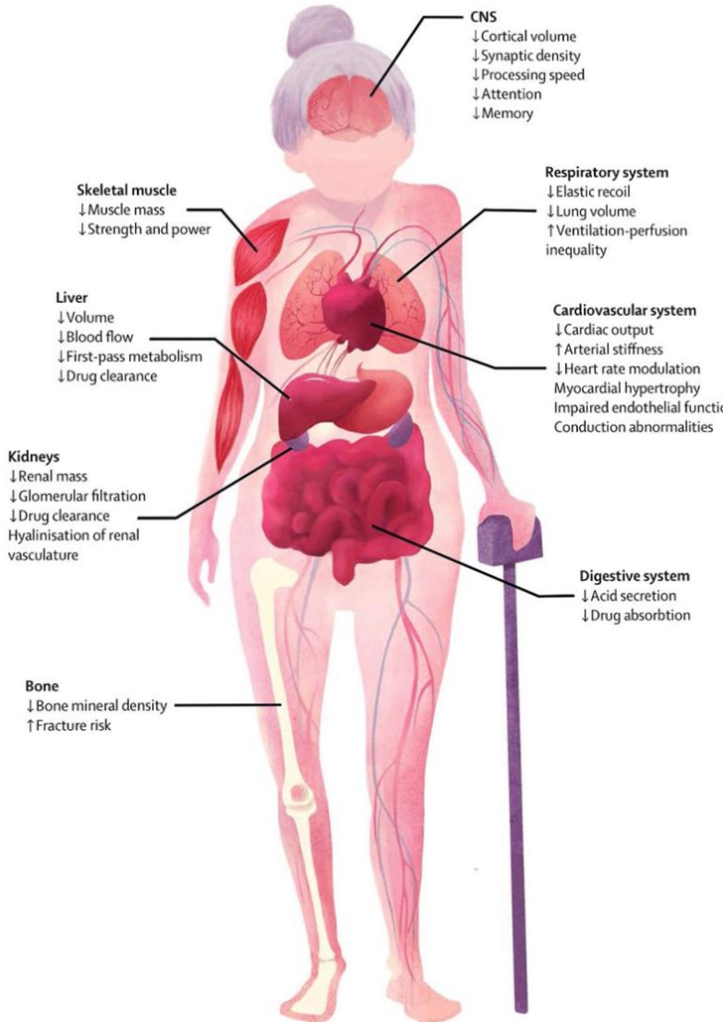
- Lung deficiency is common among elderly individuals. There is a decrease in pulmonary ventilation which means that the ability of inhalation and exhalation is decreased. The increased residual volume is another sign of ageing.
- Residual volume is the amount of air left in the lungs at the end of a maximal expiration, the lungs are never empty there is always some air to prevent them from collapsing. The residual lung volume is typically increased due to the inability to forcibly expire and remove air from the lungs. This results in accelerated lung function decline. Cardiac deficiency makes it hard for the heart to pump blood as it was easier in early life.
- The decreasing capacity of heart to function normally may cause a rise in blood pressure. The arteries stiffen gradually with increasing age and lose their flexibility over time. Nervous deficiency with decrease in the nerve conduction causes the person to slow down a bit.
- Response to a stimulus is decreased, there is prolonged reaction time to any given stimulus and, there is a significant reduction in speed of movements. Due to a decrease in cortical volume, processing information is slow, the memory is weak and attention span is shorter than before. Ageing has a bad effect on bones, the bone density decreases as the bone building cell shave a slower production rate.
- A risk of a condition called osteoporosis is increased. The risk of fractures is increased and with the damage to joint structures, there is a risk of overstretching, rupture of the structures like tendons and ligaments resulting in limited mobility.
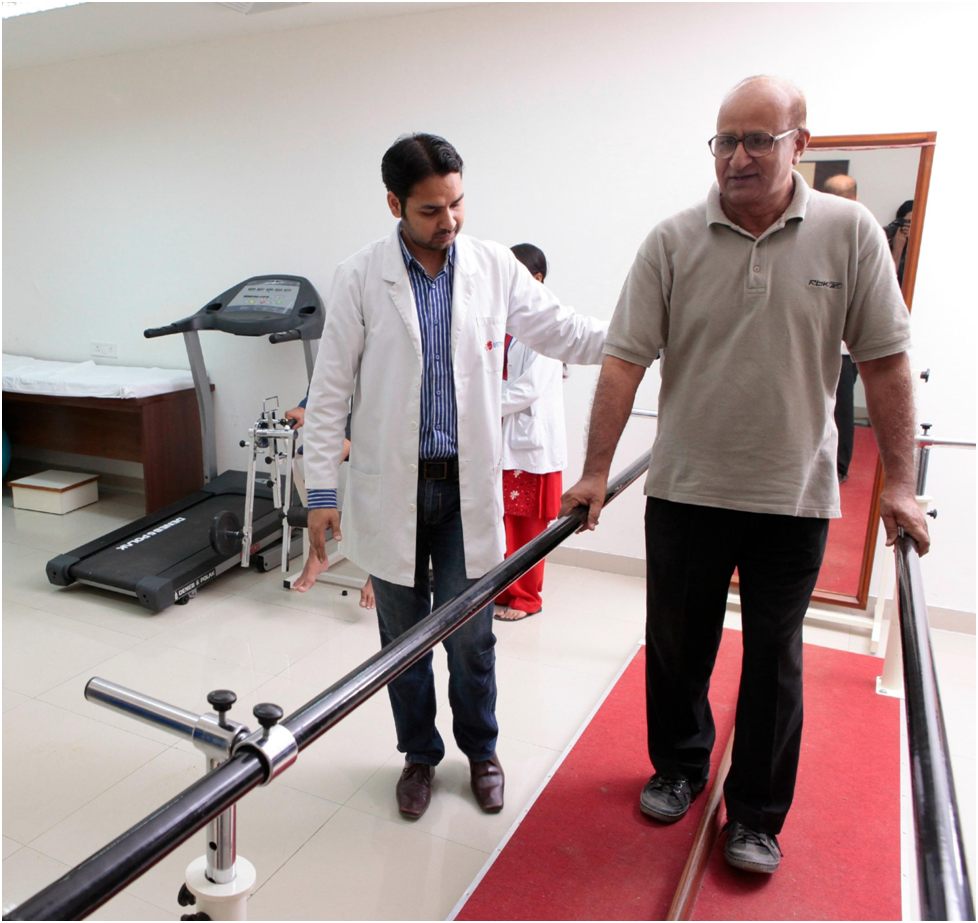
Physiotherapy in Geriatric Population

- Regular participation in physical activity of any type and/ or exercise is not only integral to the maintenance of good health and functional independence in older adulthood, but also serves as a primary role in the prevention of numerous chronic diseases for example hypertension, arthritis, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease like myocardial infarction (heart attack), osteoporosis (severe bone loss) certain types of cancer and cognitive (attention and memory retention) decline.
- It is also beneficial in keeping the brain fit and prevents neurodegenerative disorders like dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Physiotherapists at Progressive care are experts in identifying the needs of the elderly and providing a good exercise prescription. If the exercises are started early they significantlystrengthen the body and maintain the muscle mass.
- Please contact a physiotherapist for tailored exercise therapy and do not self-administer exercises without supervision.
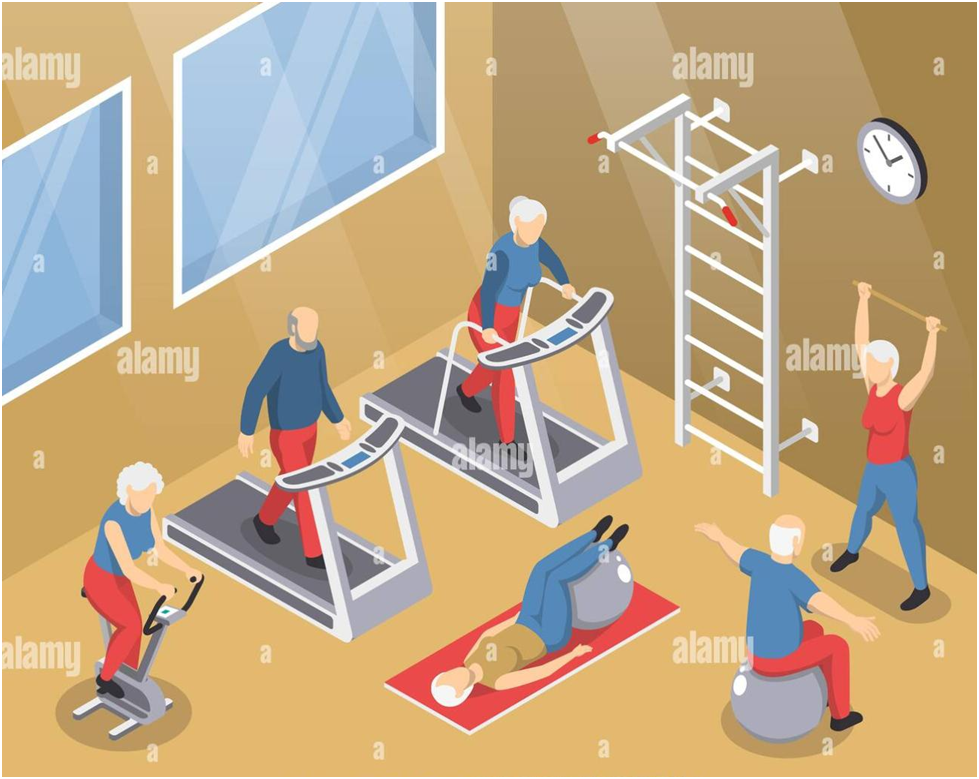

- It is imminent that inactivity doubles the risks of developing a disorder as well as disability that will adversely affect mobility as well as the ability to perform even the most basic activities of daily life. A sedentary lifestyle adds to the misery.
- This downward spiral in physical function ultimately heightens the risk of both the loss of functional independence and falls . It has been observed that free active exercises have the potential to improve functional balance and mobility in the geriatric population. The physiotherapist can help maintaining the physical activity and can guide you with acquiring a more active lifestyle.
- When fall prevention is concerned, it is possible that these frail elderly would have benefit from the resistance exercises for the leg muscles. However, ankle exercises focused on increasing ankle ROM may have an influence on reducing falls in this population, and good strength of foot muscles may improve the grip on the footwear/floor. Additionally, it has been concluded that the ankle ROM exercises have potentially worked on improving balance and reducing falls in elderly people. The physiotherapists will assess and guide you with proper ankle- foot mobility and strengthening exercises.
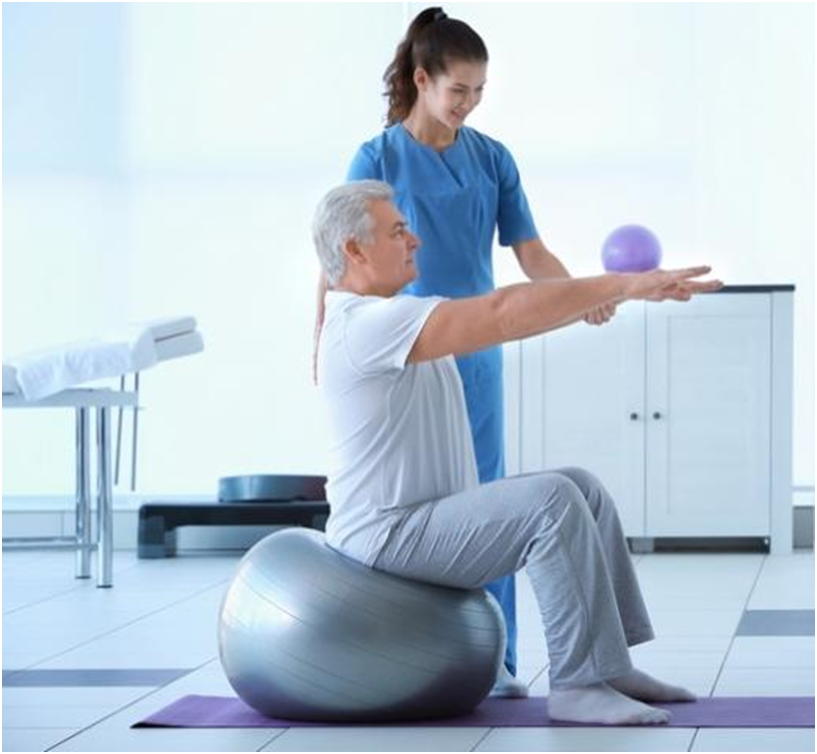

- Balance Prevention: For older adults, many activities such as squatting, standing up from a chair/bed and walking may be difficult because of postural hypotension (low blood pressure on standing) and can cause them to feel unsteady, which increases their risk of falling.

- Regular medical checkup and physiotherapy for balance is necessary for prevention in such cases. A simple sit to stand exercise benefits the elders immensely. Assistance is needed when the older people fall often and have injuries related to falls. All the necessary assistance devices like walking sticks and walking frames are available and can be prescribed by the physiotherapist.
- Cardiovascular fitness: Exercises for a healthy heart are of utmost importance for a good life. Low-intensity exercises only slightly increase the heart and breath rate. They are suitable for older adults with almost all medical conditions except respiratory problems.
- These exercises are of least exertion and are not particularly difficult or dangerous. The most standard low-intensity cardio activity is walking. Walking is proven to make the muscles pump more blood and help heart with its function. Walking at a slow pace during standard activities, such as gardening, shopping, talking on phone also counts toward the goal of fitness.
- Physiotherapists can assist with easy and doable cardiovascular exercises for the elderly individuals. Even with frail people it is possible to perform these exercises while sitting on chair. Chair-aerobics is a new trend of exercises which has proven to be beneficial for bedridden individuals. If the health and stamina improves, your physiotherapist might consider increasing the pace or length of your walks/ cardio sessions.
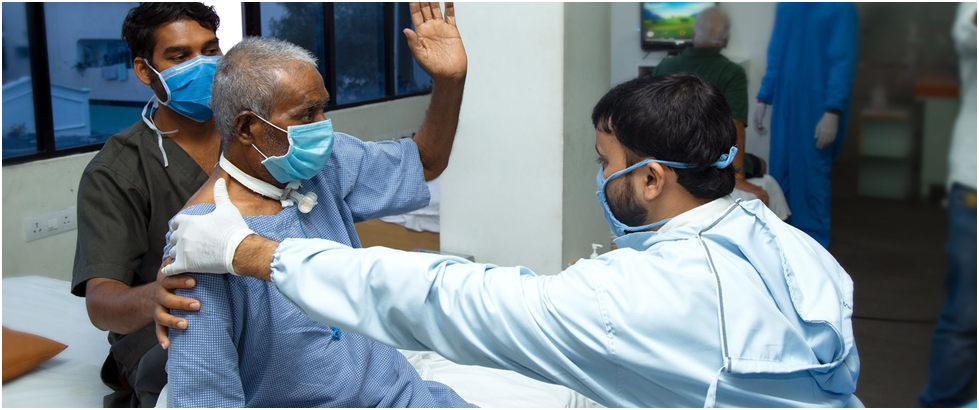
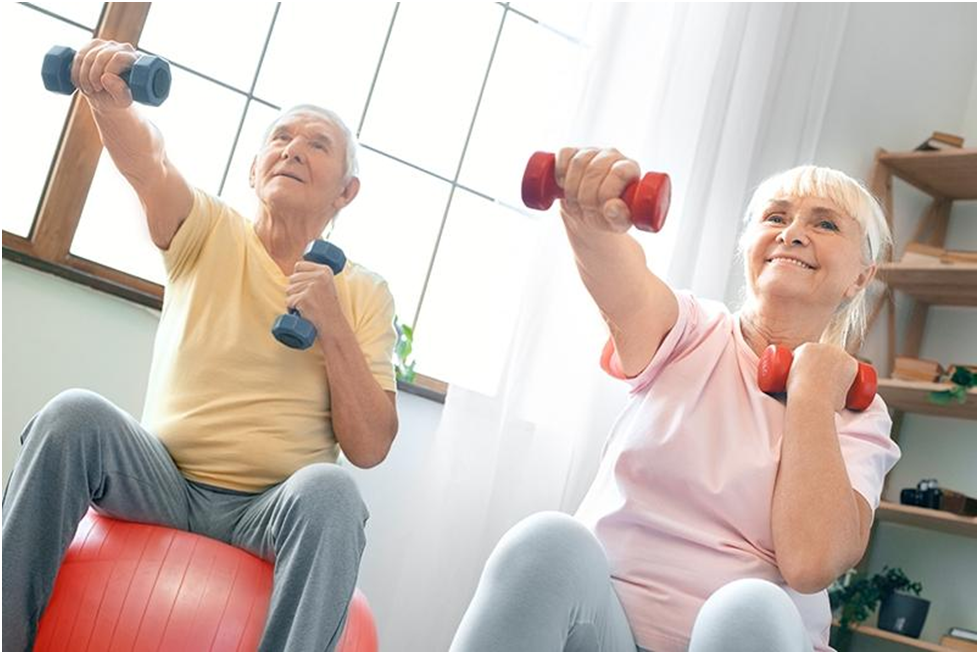
Elderly doing sitting exercises to enhance cardiovascular fitness

There are many aspects of Geriatric Rehabilitation which are holistic these include Tai chi practices, Aquatic exercise sessions, Yoga, Creative Dancing, Gardening, etc. Group exercise sessions are available at many centres with instructors. Keeping physically active is the key to prevent adverse effects of ageing.
Kindly visit your Physiotherapist to seek help with all your problems and prevent disability.
Reference:
- GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF GERIATRIC REHABILITATION Cringuta Paraschiv*, Irina Esanu, Rodica Ghiuru, Cristina Maria Gavrilescu. Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Vol. 7, No. 1, January – March 2015.
- Textbook- New Horizons in Geriatric Medicine. Volume 2 ISBN: 978-1-62808-976-9 Editors: A. T. Isik, M. R. Mas, M. A. Karan et al.
- Chapter 15: geriatric rehabilitation. Effects of exercise on cardiovascular performance in the elderly Carlo Vigorito and Francesco Giallauria.
- Aerobic exercise in the elderly: a key to successful agingJerome L Fleg. Discov Med. 2012 Mar.

Progressive Care Physiotherapy
Progressive Care Physiotherapy Management is the best service in the physiotherapy industry. It is known for providing the best service and cutting-edge technology to help speed up recovery, while also being able to offer various treatment options that are tailored to your specific needs.
For More details call us on 9618906780

